Federal certifications provides companies and individuals helpful Federal guides on a variety of pertinent subjects in understanding the Federal certification processes and procedures. Certification requirements for Federal Department and Agencies differ across the entire Federal landscape. You should refer to your customer’s specific requirements regarding the certifications necessary to add new products to their networks.
All links will open to an external site or pdf
The Department of Defense Information Network Approved Products List (DODIN APL) is established in accordance with the UC Requirements (UCR 2013) document and mandated by the DOD Instruction (DODI) 8100.04. Its purpose is to maintain a single consolidated list of products that have completed Interoperability (IO) and Cybersecurity certifications. The use of the DODIN APL allows DOD Components to purchase and operate systems over the entirety of DOD network infrastructure.
NVLAP accredited Cryptographic and Security Testing (CST) Laboratories perform conformance testing of cryptographic modules. Cryptographic modules are tested against requirements found in FIPS PUB 140-2 [pdf doc], Security Requirements for Cryptographic Modules. Security requirements cover 11 areas related to the design and implementation of a cryptographic module. For each area, a cryptographic module receives a security level rating (1-4, from lowest to highest) depending on what requirements are met.
The National Information Assurance Partnership (NIAP) is responsible for the U.S. implementation of the Common Criteria, including management of the NIAP Common Criteria Evaluation and Validation Scheme (CCEVS) validation body. NIAP manages a national program for developing Protection Profiles, evaluation methodologies, and policies to ensure achievable, repeatable, and testable requirements. In partnership with NIST, NIAP also approves Common Criteria Testing Laboratories to conduct these security evaluations in private sector operations across the U.S.
Section 508 refers to a statutory section in the Rehabilitation Act of 1973 (29 U.S.C. 794d). Congress significantly strengthened Section 508 in the Workforce Investment Act of 1998. Its primary purpose is to provide access to and use Federal executive agencies’ electronic and information technology (ICT) by individuals with disabilities.
Federal Risk and Authorization Management Program - FedRAMP - Cloud Services

The Federal Risk and Authorization Management Program, or FedRAMP, is a government-wide program that provides a standardized approach to security assessment, authorization, and continuous monitoring for cloud products and services. This approach uses a “do once, use many times” framework that saves an estimated 30-40% of government costs and the time and staff required to conduct redundant agency security assessments.
FedRAMP is the result of close collaboration with cybersecurity and cloud experts from the General Services Administration (GSA), National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), Department of Homeland Security (DHS), Department of Defense (DOD), National Security Agency (NSA), Office of Management and Budget (OMB), the Federal Chief Information Officer (CIO) Council and its working groups, as well as private industry.
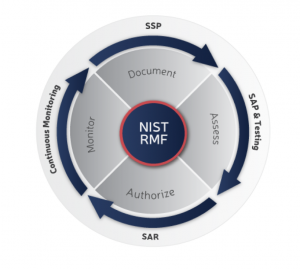
Risk Management Framework (RMF) is the unified information security framework for the entire federal government that is replacing the legacy Certification and Accreditation (C&A) processes within federal government departments and agencies, the Department of Defense (DOD) and the Intelligence Community (IC).
NOW RMF: The Networthiness Certification Program, now replaced by the RMF, was the legacy means to manage risks and impacts associated with the fielding of Information Systems (ISs) and to support efforts to sustain the health of the Army Enterprise Infrastructure.
After completing a security assessment, the head of an agency (or their designee) can authorize the system for use or grant an Authorization to Operate (ATO). An agency grants an ATO using a risk-based framework that analyzes how vendors implement security controls within their IT environment.